
Capitalism has done to William Morris what it always does best to political creatives: de-politicized his legacy for profit.
As a devoted William Morris fan, it’s been a delight — in part — to see Morris & Co prints brought to high streets across the world by H&M and rendered instafamous. Morris’ beautifully stylized depictions of nature are almost ubiquitous now.
These mediaeval-inspired designs were originally produced for Victorian wallpapers and home textiles, and their imposing yet delicate grandeur established Morris as one of the 19th century’s most famous textile designers. Now the popularity of this clothing collaboration has launched his work into the international spotlight. But just what tradition is being celebrated by H&M marketing his work as iconically British? Just what are we losing when we strip an artist’s work of its political context?
![]()
In addition to being a poet and designer, Morris was also a revolutionary and friend of Marx and Engels. He was an idealist who argued that craftwork and cooperation would make wage labour obsolete and, far from being simply the “iconic [nineteenth Century] British wallpaper and fabrics brand” which H&M proffers, Morris’s company was run on collective principles and managed by his daughter May at a time when women were rarely afforded such power.
Capitalism has done to William Morris what it always does best to political creatives: de-politicized his legacy for profit. Admittedly his household designs have long been mass-produced and on sale in museums and homeware shops. But at least the mugs, coasters and tea towels were affordable symbols of affinity with Morris. They were often marketed within the confines of the designs’ history and therefore, by and large, did not so fully erase his politics.
Just what are we losing when we strip an artist’s work of its political context? Click To TweetH&M presents his maximalist, repeated homages to the natural world as emblems of British tradition and nostalgia, when in fact Morris used mediaeval aesthetics not to celebrate Britain, but rather as a protest in advocating pre-industrial values. The press, however, has followed H&M’s marketing wash, instead of looking to Morris’s actual political legacy.
Vogue termed it “another British heritage brand”; The Guardian, too, echoed the “heritage” language.
How does capitalism’s own tradition of depoliticization play out when consumers are clothed in imagery taken out of context but also place, having originally been created to celebrate home?
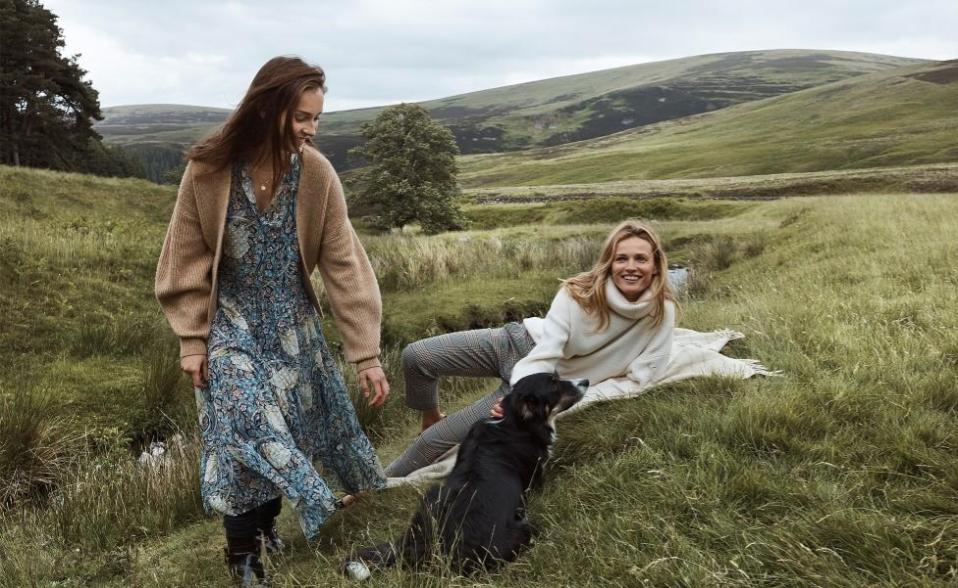
H&M is curating a selective history which conjures nostalgia for a Victorian era of Empire. They launched their Morris and Co collaboration with a campaign video boasting a grainy, faux ’70s aesthetic.
Skinny white women prance through what looks like the Scottish Highlands, a brook and a cottage to their backs. They wear silk scarves, maxi dresses, pussy bow tops: demure looks paired with classic jumpers and jeans. Then, in a move which reinforced the capitalistic juggernaut that is H&M’s marketing, the company then gathered influencers for “paid partnerships” at the Morris-decorated mansion Standen House.

This manipulation fits within fashion’s long history with the commodification of radical craft and the history of Morris prints is simply a case study of how mainstream consumerism subsumes radical aesthetics.
Two previous uses of Morris designs for clothing aimed to pay tribute to his anti-establishment politics by linking them to subcultural styles.
The first was in the ’60s when autodidact designer Mary Quant — inspired by Mod fashion and the sexual revolution — made a mini-skirt suit in Morris’ “Marigold” print. The second instance occurred in 2017 when fashion house Loewe released a capsule collection approaching Morris through punk style.
However, both fell into the consumer culture trap where radical social movements were transformed into fashionable commodities for companies to profit from.
The aesthetics of subcultures — like punk for example, which communicates a rejection of the status quo and an alternative belonging — also resided within the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood and the Arts and Crafts movement (of which Morris was a leader) in their distancing from Victorian production and values.
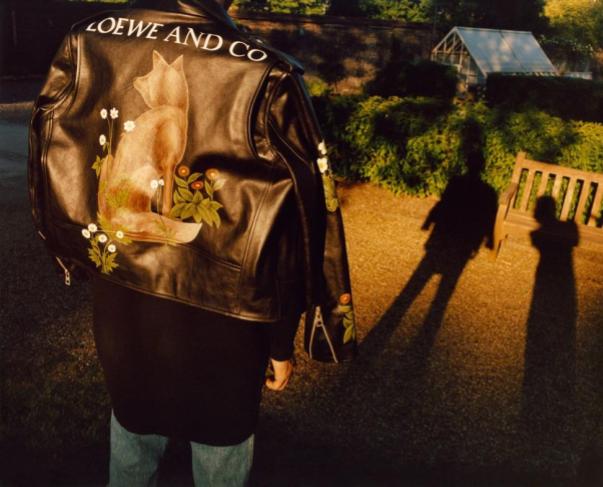
When aesthetics designed to be imbued with a certain meaning are donned as decontextualized fashion statements, those meanings are signaled without an actual affinity for movement, without a desire to belong or perpetuate the aesthetics’ accompanying ideals. This transformation — problematic in itself — is the process of reincorporation which leads to meanings being written over at best and bastardized or erased at worst.
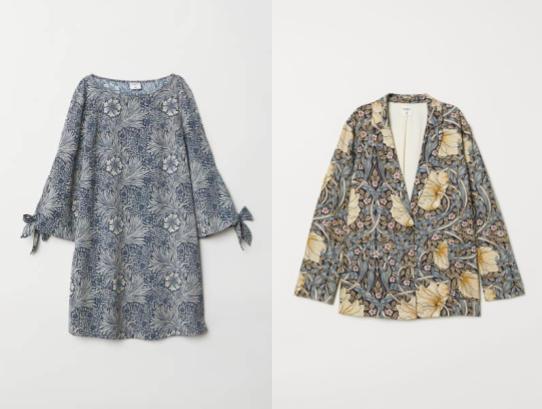

Looking at the H&M collection, we can see nods to this lineage of aesthetic spin-offs, although they don’t directly mention the homage.
Their ’60s-esque mini dress uses the same print as Quant’s mini-skirt suit and their “Pimpernel” trouser suit recalls George Harrison in a “Golden Lily”-patterned blazer or John Lennon in “Chrysanthemum.”
Morris’ politics inspired some subcultural affinity in the 20th Century but the sartorial trickle-down of these styles is mere commodification.

The anti-establishment message has disappeared when a mainstream brand like H&M calls him “iconic.” yet simultaneously ignores the radical politics he stood for. Indeed, when the company talks about “tradition,” they don’t even mean this tradition of subversive reuse. Instead, they invoke an abstract, white, and classist British status quo of countryside leisure.
Returning to the bigger picture of how fashion commodifies art, the connection between Morris’ radicalism and subcultural fashions like mods and punks is fitting — but not for the reasons the fashion houses intended.
Dick Hebdige, scholar of subcultural style, coined a term for the way capitalism seizes subversive aesthetics and turns them into a “fashion,” therefore making them apolitical, mainstream and profitable: “reincorporation.”

In his book Subcultures: the Meaning of Style he argues that youth movements develop their own style which puts across their criticisms of the existing order. The mainstream culture, however, incorporates their subversions within its own pre-existing world-view. In this way, the deviant meaning is lost. This sort of commodification happened to the styles of teddy boys, mods and rockers, hippies, skinheads, punks, etc., but it also happens today when far older styles with a political message are brought into vogue.
William Morris’s natural imagery — inspired by mediaeval styles because it sought to evade capitalism — now adorns the high street as season-appropriate florals.
Paying attention to the intended meanings behind art and design is important, especially when corporate fashion aims to depoliticize and commodify those visions’ intentions. Fashion is political, and the imagery it recycles, especially so.
William Morris’ creations were inspired by his belief in ordinary people’s value and rights; his words still appear on trade union banners today. Dismantling the homogenizing consumerism of fashion means celebrating the hidden radical histories erased by corporations, whether those be the politics of class, race, gender or sexuality.

So when you next see someone in that instafamous H&M x Morris & Co. maxi dress, they are — arguably — an inadvertent, living homage to a Victorian anti-Capitalist aesthetic and to those who sought revolutionary in the ’60s and ’70s.
There’s a thin line between buying pleasing patterns and communicating affinity of ideals, but if we celebrate and talk about these hidden histories we foster a critical eye and a celebration of the subversive role fashion should be allowed — and continue —to play.

